杂题
Nepnep2025 Lattice Bros
1 | #已知α的极小多项式为三次多项式f(x),即f(α)=0,且α≈54236.606188881754809671280151541781895183337725393 |
首先我们需要恢复的是a0的值
我们可以利用LLL算法来恢复一定次数的极小多项式,对于多项式来说我们有 a0 + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 = 0
$$ \begin{pmatrix} a_0&a_1&a_2&a_3 \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix} 1 &0& 0 & a^0M\\ 0& 1 & 0 & a^1M\\ 0&0& 1 & a^2M\\ 0&0& 0&a^3M \end{pmatrix} $$
这里我们M我们根据a的的精度选择10^50来配平
1 | a=54236.606188881754809671280151541781895183337725393 |
这里其它师傅那里看到了sagemath的内置函数可以求解
1 | alpha = 54236.606188881754809671280151541781895183337725393 |
得到a0之后我们可以直接求出p
之后就是HNP问题了
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
Nepnep2025 ezRSA2
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import getStrongPrime, getRandomNBitInteger, GCD, inverse, long_to_bytes, bytes_to_long, sieve_base |
审计代码发现这里是关键函数
1 | hints = [] |
这里我们可以得到hint的同余方程组 $$ \left\{ \begin{array}{l} \operatorname{hint}_{0} \equiv d \ (\bmod \ sieve_base[1]) \\ \operatorname{hint}_{1} \equiv d \ (\bmod \ sieve_base[2]) \\ \cdots \\ \operatorname{hint}_{r} \equiv d \ (\bmod \ sieve_base[i]) \end{array} \right. $$
同时还可以得到M的等式 $$ M=\prod_{i=1}^{len(sieve_base)}sieve_base[i] $$
我们可以先用crt来恢复部分的d
之所以这里只能恢复部分的d是因为
crt可以让我们从 d mod li 的这些余数中,计算出 d mod M
所以我们得到的是d在模M下的值,即 d ≡ d0 mod M
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
这里求出了d0即是部分的d,部分私钥泄露会想到用Cooper来打
这里看到RSA的等式 e(d0 + k0 * M) − 1 = k1(N − p − q + 1) d=d0+k*M
有等式 e * (d0 + k * M) − 1 = k2(N − p − q + 1) 这里考虑用⼆元copper来打,先对等式进行变形 1 − e * d0 + k(N + 1 − r) ≡ 0 (mod e * M) 这样的式子就可以打了
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
DASCTF2025 Strange RSA
1 | import random |
题目分为两个部分,一部分是对hint的加密,一部分是对flag的加密
我们先解出hint
1 | def generate_hint_params(u, v, keysize=512): |
这里我们发现可以用Boneh-Durfee攻击来求d1,d2
这里先看u,v和d1,d2的生成表达式
1 | u = random.randint(2, 1 << 26) |
从这里我们知道d1,d2<2256 + 26,这里d > N292
满足Boneh-Durfee攻击,这里格的大小取8
1 | from __future__ import print_function |
这里观察到x是d1和d2的最大公因数
1 | x = gcd(d1,d2) |
求出x后u,v就很简单可以直接求出了
这里的hint知道是广义RSA
搜到这篇paper
根据论文中
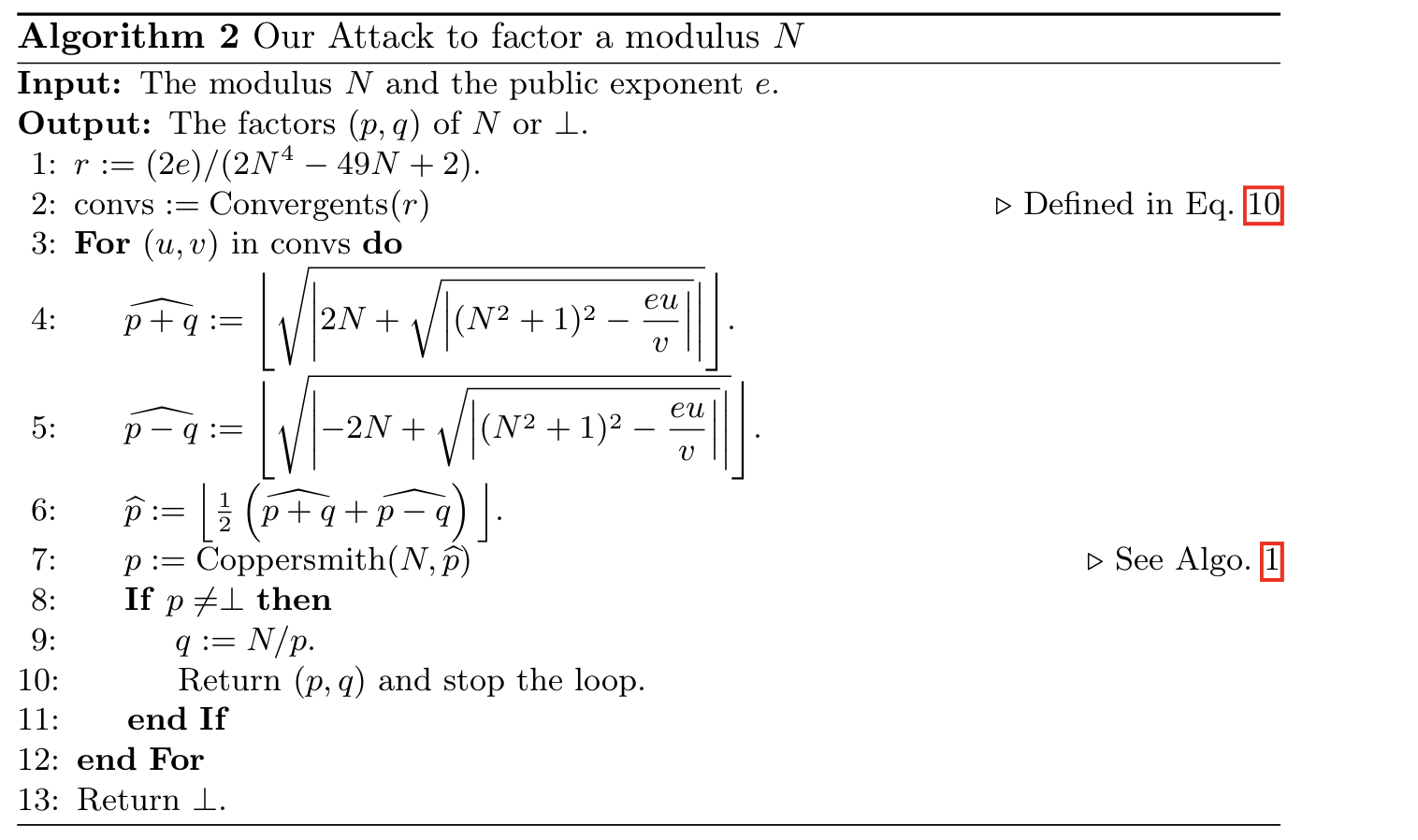
论文给出了怎么求p,q是通过先求出p的近似值在打cooper求的
这里是先求出$\widehat{p+q}$ ,和$\widehat{p-q}$ 再将两式除2得到p̂,然后打cooper
这里论文中u,v好像是通过连分数展开r求得的,但是我试了一下好像没有得到(不知道是不是我理解错了),但是对这道题没有什影响
得到p后就是常规的RSA了
1 | from gmpy2 import mpz, sqrt, mpfr, get_context, is_prime, powmod |
Deadsec CTF2024 Raul Rosas
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
题目不难读懂,感觉有很多奇技淫巧来解
首先来审计代码,这里的代码十分简洁
给我们p1是一个1024bit的数,并且将其转为二进制
然后p2是取p1前419位,后面空出的位数用0来补齐
接着取p2的下一个素数
q1,q2的数量级都是300bit
最后给出了n1,n2 n1 = p12 * q1
n2 = p22 * q2
因为这里的p2是取p1的前419位,所以n1,n2大概也是相近的
所以用连分数展开 $$ \frac{n1}{n2} \approx \frac{q1}{q2} $$
1 | n1=33914684861748025775039281034732118800210172226202865626649257734640860626122496857824722482435571212266837521062975265470108636677204118801674455876175256919094583111702086440374440069720564836535455468886946320281180036997133848753476194808776154286740338853149382219104098930424628379244203425638143586895732678175237573473771798480275214400819978317207532566320561087373402673942574292313462136068626729114505686759701305592972367260477978324301469299251420212283758756993372112866755859599750559165005003201133841030574381795101573167606659158769490361449603797836102692182242091338045317594471059984757228202609971840405638858696334676026230362235521239830379389872765912383844262135900613776738814453 |
这样就得到了q1和q2
1 | q1,q2 = 1226422900699937313306345486827490610540478397988332672940596868693721441368094739238893997,1651764208712002362909070586532659043033781575172011989418709627827265240039573208353001543 |
接下来就是解RSA了
1 | import gmpy2 |
还有个是用二元cooper来打的 n2 = p22 * q2 = (x * 2605 + plow)2 * y
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
idekCTF 2025 Diamond Ticket
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
这里出题人的wp
首先是题目给出了一个自定义函数,我们还知道其中a,b,p的值
1 | def chocolate_generator(m:int) -> int: |
然后给出一下的代码
1 | #The diamond ticket is hiding inside chocolate |
生成1337个随机数,其中范围是(1,p)然后存入chocolate_bag中
再将flag_chocolate加入chocolate_bag的末尾
remain是取chocolate_bag的最后五位数,然后将这个五个元素拼接为字节串
接着又是一个新的加密
1 | P = getPrime(512) |
这里很明显用共模攻击可以直接打,那么可以恢复出remain_bytes
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
现在我们可以列出方程 c ≡ am + bm (mod p) 我们不妨令b = ak,那么我们就有 c ≡ am + (ak)m (mod p)
c ≡ am + (ak)m (mod p)
现在再令X=a^m,那么就有方程 c ≡ X + Xk (mod p) 解这个X的trick在这里
我们可以先求出k
1 | p = 170829625398370252501980763763988409583 |
根据上面的列出方程
1 | p = 170829625398370252501980763763988409583 |
然后就是在解一个离散对数
1 | m = GF(p)(X).log(a) |
1 | p = 170829625398370252501980763763988409583 |
这里求出的m是m%p后的结果
1 | load('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TheBlupper/linineq/refs/heads/main/linineq.py') |
idekCTF 2024 Golden Ticket
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
上题就是在这题的基础上进行改进
golden_ticket:将flag数值化后的结果 flag_chocolate = chocolate_generator(golden_ticket) p = 396430433566694153228963024068183195900644000015629930982017434859080008533624204265038366113052353086248115602503012179807206251960510130759852727353283868788493357310003786807 返回 (pow(13, golden_ticket, p) + pow(37, golden_ticket, p)) % p chocolate_bag = [] 对于0以上、golden_ticket未満的i,执行以下操作: 将chocolate_generator(i)添加到chocolate_bag中 将flag_chocolate添加到chocolate_bag中 remain: chocolate_bag的最后两个元素 输出remain
我们有
1 | (x + y) % p = c1 |
$$
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
WHYCTF 2025
substituteteacher
1 | "Lcb gpzs tpvcbx phpzsvl ewig lgbsmc mwpl, bpmc xgwj p lzse, mwtx pmmivplzws. Pswlcbg dzvvzsh jbgvws mpvb, pswlcbg xbpx bsx, pswlcbg dzvbgpytb Libvxpe. Xblbmlzub Dztbv Mwgyzs, lcpl'v ewi, psx ewig miggbsl tbpx (p mgejlzm, fplbg-xpdphbx swlb rwisx zs p jzhbws'v sbvl – xws'l pva) cpv ygwihcl ewi lw lcb bxhb wr lcb zsrpdwiv Gpubsfwwx Fwwxv. Twmptv fczvjbgbx lptbv wr vlgpshb tzhclv psx bubs vlgpshbg xzvpjjbpgpsmbv. 'Jgwypyte kivl p jpglzmitpgte phhgbvvzub ypxhbg,' ewi'x dillbgbx lw ewigvbtr, yil lcb isbpvb zs ewig hil lwtx p xzrrbgbsl vlwge. |
直接用quipqiup解密即可得到
1 | "The rain lashed against your trench coat, each drop a tiny, cold accusation. Another missing person case, another dead end, another miserable Tuesday. Detective Miles Corbin, that's you, and your current lead (a cryptic, water-damaged note found in a pigeon's nest – don't ask) has brought you to the edge of the infamous Ravenwood Woods. Locals whispered tales of strange lights and even stranger disappearances. 'Probably just a particularly aggressive badger,' you'd muttered to yourself, but the unease in your gut told a different story. The path, if you could even call it that, dissolved into a muddy, overgrown track. Ahead, barely visible through the downpour, a faint flicker of light. A cabin. Wooden, dilapidated, and looking like it had swallowed more than a few secrets. 'Well, Miles,' you sighed, 'you've certainly seen worse invitations to tetanus.' You push open the creaky wooden door. The smell of damp earth and something vaguely metallic, like old pennies, fills your nostrils. As you step inside, a sudden, heavy THUD echoes behind you. The door slams shut. You try the handle. Locked. And no amount of jiggling, rattling, or polite pleading seems to make a difference. "You are in a dimly lit, rectangular room. The air is thick with the scent of damp wood and something undefinable, perhaps just the lingering dread of forgotten lives. Rain streaks down the single, grimy window on the far wall. A crude wooden table, two rickety chairs, and a dusty, moth-eaten rug are the only furniture. A small, unlit fireplace sits against one wall, its hearth filled with cold ashes. On the table, a flickering oil lamp casts dancing shadows. Next to the lamp lays a notebook with the following text scribbles on it: flag{bd96db352436ef4f8ec6cada5979b038}." |
somkracht65537
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
题目十分简洁
1 | ct1 = pow(msg, e, N) |
这样的式子一看就是可以打共模攻击的,但是这里p+q的值不知道
由欧拉定理可以知道
如果gcd(m,N)=1 mφ(N) ≡ 1 (mod N) 对于任意整数 k有 ma ≡ ma + kφ(N) (mod N) 指数可以加上(或减去)φ(N) 的倍数而不改变结果
这就是幂在 φ(N) 的周期性
那么知道这里后面就简单了 ct2 = msgp + q mod N
ct2 = msgp + q + φ(N) mod N
ct2 = msgp + q + (p * q − p − q + 1) mod N
ct2 = msgN + 1 mod N
接下来打个共模攻击就好
1 | import gmpy2 |
